A Simple Example
Recursive functions are functions that call themselves. Recursive algorithms are generally used when the
data is self-similar at different scales. Trees, linked lists, and sequences are often processed with recursive algorithms.
When writing a recursive function, , you are breaking the entire problem down step by step until the remaining problem is
simple enough to solve directly. This simple solution is normally known as the terminating condition or the base case.
Then, the solution can be built up from the base case to full solution.
Here is a simple example, reversing an array.
var rev = function(arrToReverse) {
if(arrToReverse.length === 1) {
return arrToReverse;
} else {
return rev(arrToReverse.slice(1)).concat(arrToReverse[0]);
}
}
So, rev([1, 2, 3]) => [3, 2, 1].
How does this work. Well, the base case is an array of length 1. In this case, the function just returns its argument, since the
reverse of a single element array is just the array. So here, the problem has been broken down to something that can easily
be solved, the reverse of a single element array. If the array is longer than one element, the function calls itself on with
the array without the first element (arrToReverse.slice(1)), appends the first element (arrToReverse), and returns that
value. Note that Array.push does not work here because it mutates the array and returns the number of elements in the mutated
array, and we need a function that returns a new array with the element appended. Array.concat is that function.
Here is another way to look at it:
rev([1,2,3]
rev([2,3])
rev([3])
return [3]
return [3,2]
return [3,2,1]
So, at each recursive step, we are reversing a smaller array until the array length is 1. At that point, we return the single
element array. At each subsequent return step, the array grows by one until the last return where we return the entire reversed
array.
Iteration can be implemented as recursion
Thing of iteration as enumerating a sequence and passing it repeatedly to a function, one function call for each value
in the sequence. Here is some code:
var looper = function(start, end, body) {
if(start > end)
return end;
else {
body(start);
return looper(start+1, end, body)
}
}
This implements the typical for loop where a numeric iteration variable is incremented by one each time through the loop.
looper(1,3, x=>console.log(x)) => 1 2 3
Looking at the code, the if statement terminates the loop (there is not a recursive call in the true branch). If the loop is
not terminating, the function is called recursively with the next element in the sequence as the start value. So the base
case is start > end. Since loops are typically used for side effects, looper returns the end value, a fairly useless return
value that is like many others in JavaScript.
Recursion in Tree Structures
var myObject = {abc: 1,
def: 2,
ghi: {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: {
"first": 1,
"second" :2
},
d:3
},
jkl: 3,
mno: 4
}
var getKeys = function(obj) {
return Object.keys(obj).reduce((acc, key) => (typeof(obj[key]) === 'object') && (!Array.isArray(obj[key])) ?
acc.concat(key, getKeys(obj[key])) : acc.concat(key), [] );
}
Here is the problem - you need to enumerate the keys in a JavaScript object. There is a nice function to do that -
Object.keys(). So, call Object.keys(myObject) to get [ ‘abc’, ‘def’, ‘ghi’, ‘jkl’, ‘mno’ ]. Oops, what happened to
a, b, c, d, first, and second. Well Object.keys() only enumerates keys an the top level object, not on nested objects.
Nested objects can be represented by trees, like this:
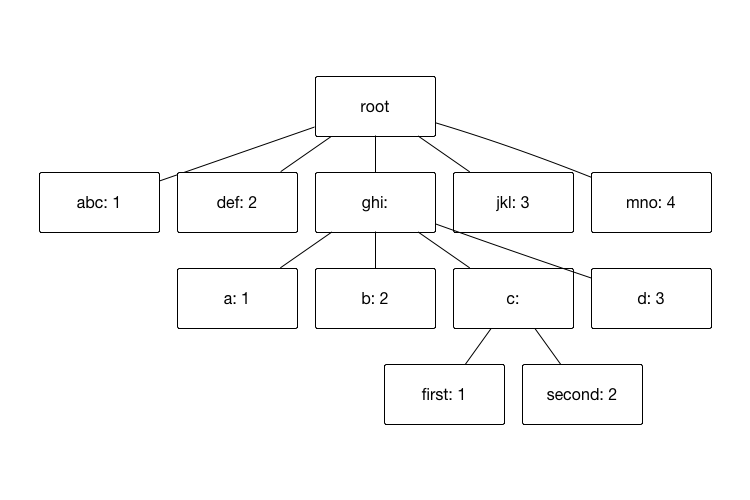
So here, we have a tree of variable arity (each node can have a different number of children), like the DOM. To enumerate
all the keys, we need to walk the tree. Looking at the getKeys function, it enumerates the keys at the current level
using Object.keys(obj). This returns an array of the keys in the top level object. We then reduce the array to go across
all the keys. The base case is when the type of the entry is not an object -
(typeof(obj[key]) = ‘object’) && (!Array.isArray(obj[key])) is false. The second part of the conditional is needed
becouse typeof(array) => ‘object’. So in this case, we just concat the key into the accumulator - the array holding
all the keys. If it is an object, we recurse and concatenate the result of the recursive call (an array) to the accumulator.
This results in an array with all the keys at this level and all the keys at the lower level.
Drawbacks
Recursion is a very flexible way to process data structures. The downside of recursion is that every recursive call incurs
function call overhead, including a stack frame. Since the stack ususally has a finite maximum size, a function with deep
recursive calls can generate an exception by blowing the stack. Many languages with functional features can optimize certain
types of recursive calls (tail recursion) eliminating these problems. Here is more information on
tail call optimization.
